One of the key challenges in customer relationship management is balancing short- and long-term Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) perspectives. Is it better to accept a lower profit now for the potential of a higher, though uncertain, future gain? Should companies invest in customers today with the hope of reaping greater rewards in the future, and if so, how much? These are just some of the dilemmas marketers face. Traditionally, there is a strong temptation to focus on quick profits at the expense of building long-term relationships with customers. However, in today’s highly competitive marketplace, strategically combining short-term gains with long-term customer value is becoming crucial for a company’s survival and growth. Machine learning offers a unique solution to help balance these two perspectives.
Short-term vs long-term customer value
Short-term customer value refers to the immediate revenue generated from a single transaction or a brief customer interaction. Examples of activities aimed at maximizing short-term value include short promotional campaigns, aggressive sales strategies, or rapid remarketing efforts. The primary goal here is to generate quick profit, often through discounts, price cuts, or “buy now” offers designed to encourage immediate purchases.
In contrast, long-term customer value reflects the total worth a customer can bring to a company over several years. In this case, it’s not just about how much a customer spends in a single transaction, but also their loyalty to the brand, frequency of return, recommendations, and influence on other customers. Strategies focusing on long-term value aim to build lasting relationships, engage customers, and create experiences that foster satisfaction and loyalty.
Machine learning (ML) and maximizing customer value
Machine learning (ML) is revolutionizing many aspects of how companies manage customer relationships. Advanced predictive models can forecast a customer’s potential value over a specified time period, taking into account not only past and present purchases but also a customer’s interactions with the brand, their engagement in marketing campaigns, and many other variables.
With accurate predictions, companies can tailor their strategies to target specific customer segments. For instance, they might invest more in customers with high long-term potential or focus on maximizing the short-term value of customers less likely to remain loyal. The matrix below illustrates different approaches for customers based on their estimated value to the company.
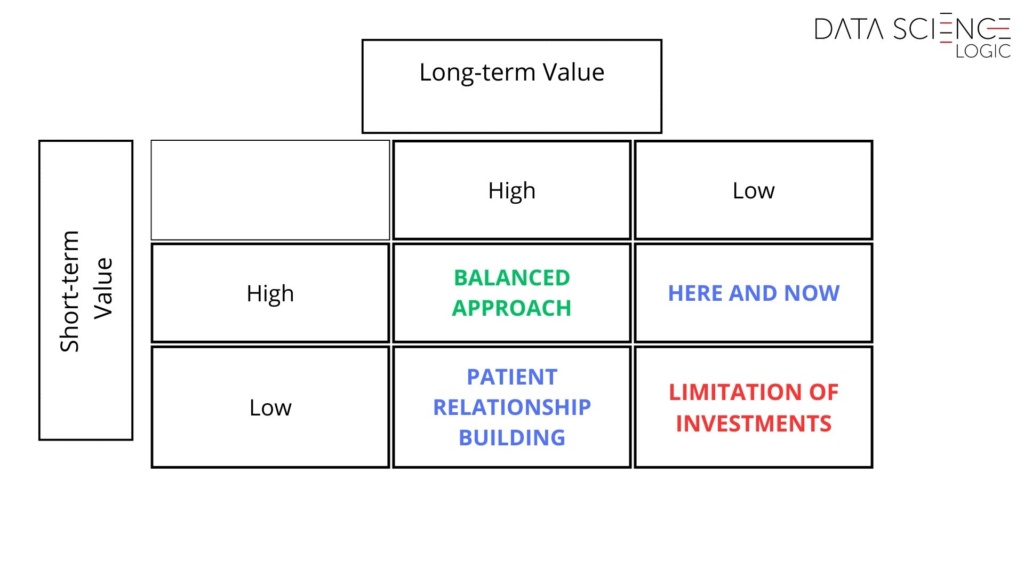
The key to successfully implementing this approach lies in the precise prediction of customer value across both timeframes. Achieving this level of accuracy is nearly impossible without leveraging machine learning, especially when dealing with large consumer bases.
Machine learning capabilities
While this example divides customer value into two categories—short-term and long-term—machine learning allows for much more granular segmentation. Predictive models can be developed for any number of time horizons, tailored to the specific needs of a consumer base or industry. Moreover, machine learning is not limited to simplistic high/low classifications. In practice, it allows for far more nuanced predictions.
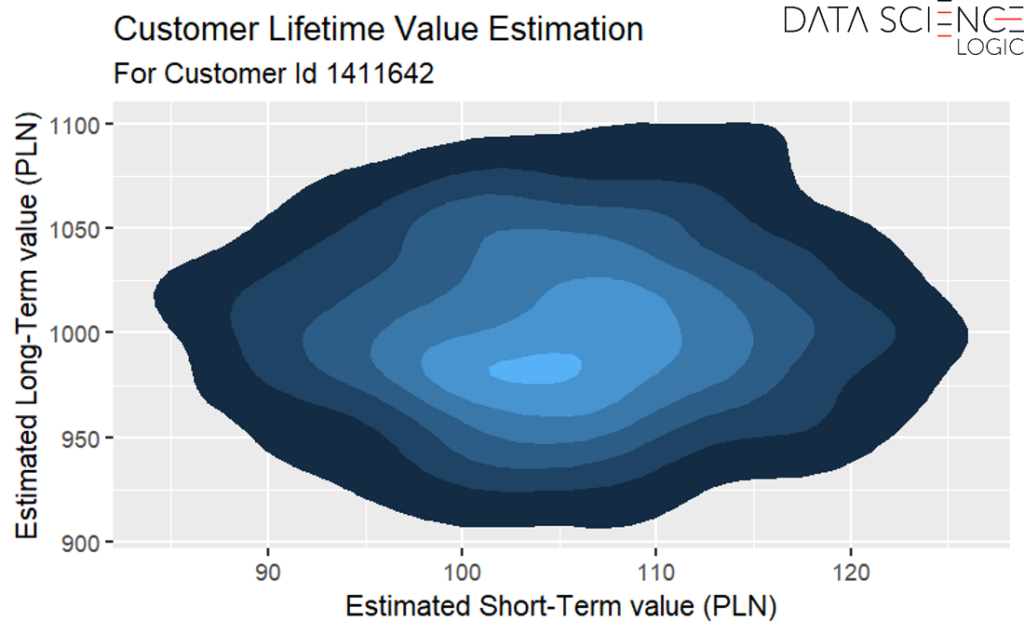
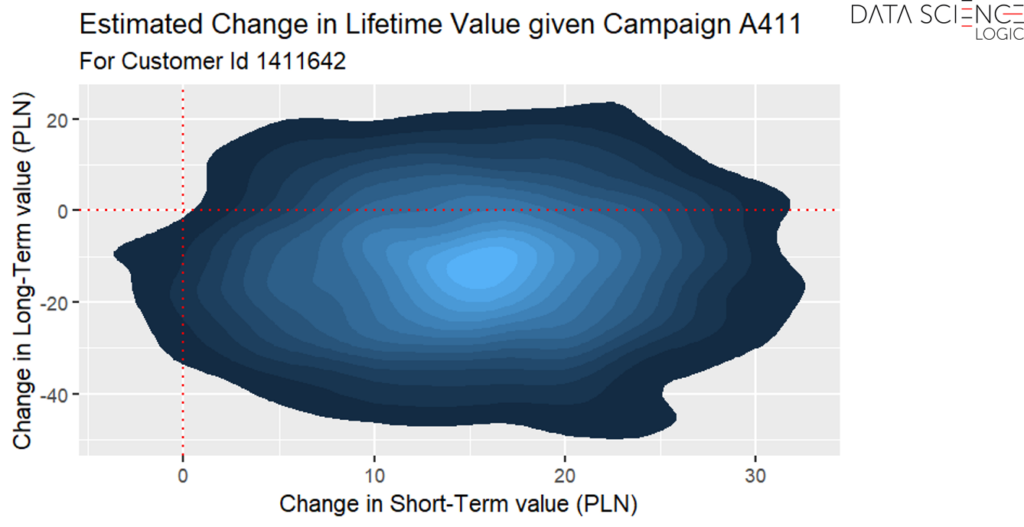
Moreover, it is also possible to estimate precisely how qualifying a particular customer for a particular campaign will affect his short- and long-term value. In the example below, a campaign with the code A411 for a customer with id 1411642 is very likely to increase his short-term value – the vast majority of the area to the right of the red vertical line indicating 0 (no change). However, the model estimates that the impact of this campaign on the customer’s long-term value will be rather negative – the vast majority of the area below the horizontal red line indicating 0 (no change) in the long term.
Summary
Balancing short-term and long-term customer value remains one of the greatest challenges for marketers. Thanks to machine learning, companies no longer have to choose between quick profits and long-term customer loyalty – they can pursue both simultaneously.
In practice, this means algorithms can predict which customers will bring the most long-term value, helping companies focus on relationship-building with them, while optimizing quick sales campaigns for less loyal customers. Machine learning helps prevent “marketing myopia,” where companies focus solely on short-term gains at the expense of future loyalty.
The future of marketing will rely on even more sophisticated predictive, optimization, and automation models, enabling businesses to fully maximize the potential of each customer – both in the short and long term.